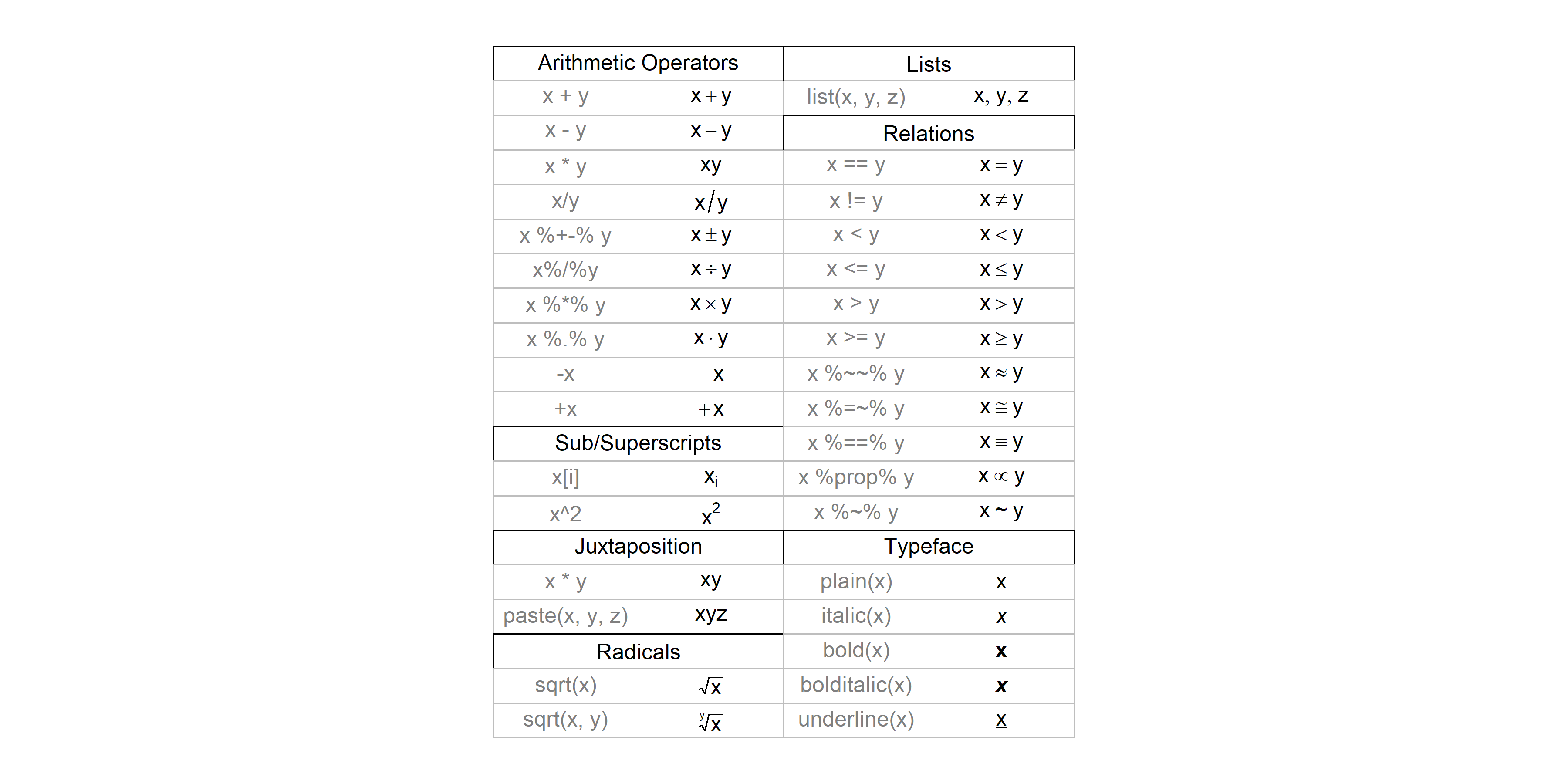
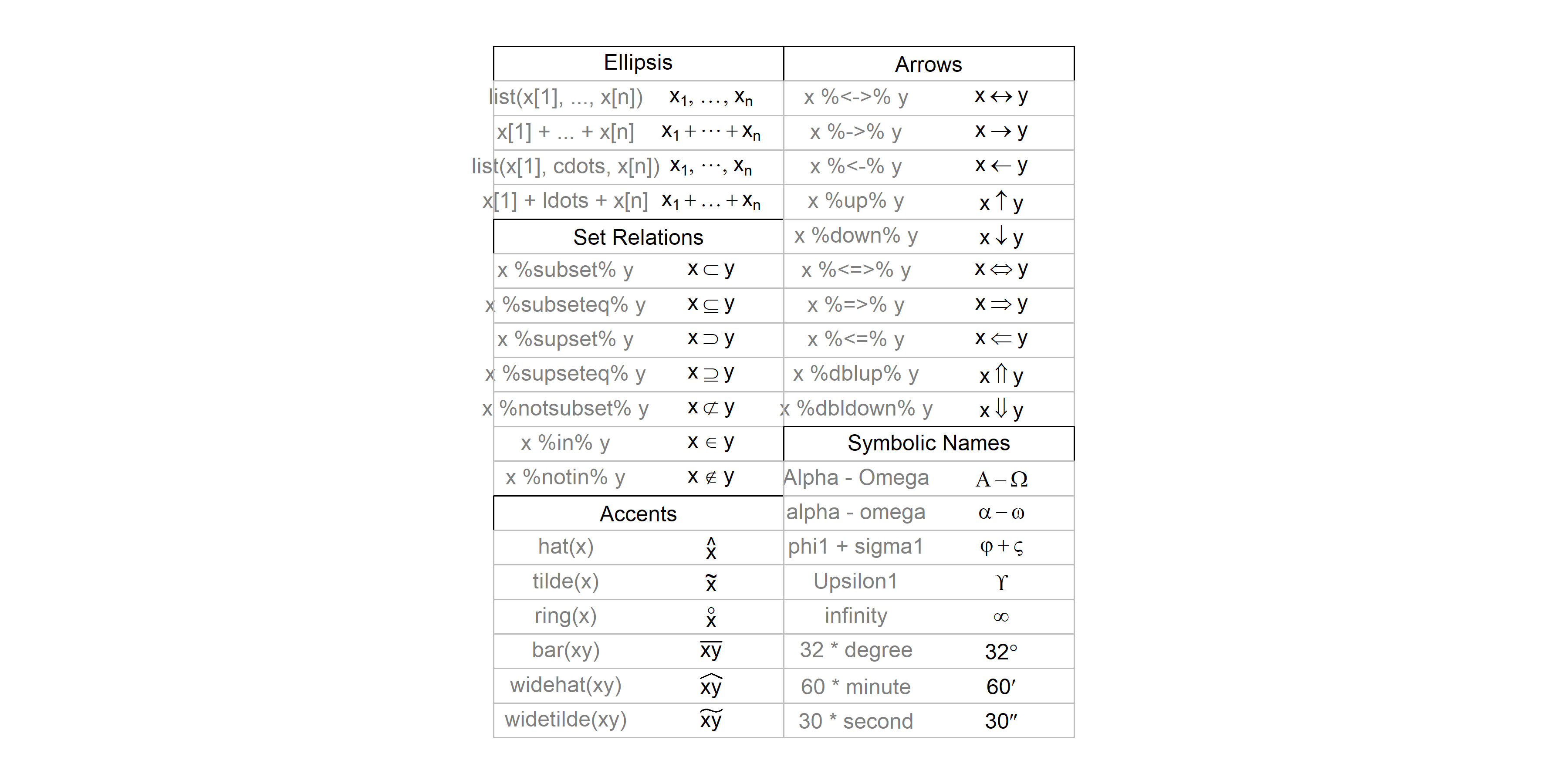
Annotations mathématiques
Pour ajouter des annotation mathématiques à un graphique, comme une équation, on aura recours à la fonction expression. Les expressions qui peuvent être utilisées sont présentées en détail dans l’aide en ligne de plotmath, visible également sur http://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/grDevices/functions/plotmath.
Combiner texte et expression
On aura recours à la fonction paste à l’intérieur de l’appel à expression. Un exemple :
# données aléatoires
df <- data.frame(x = rnorm(100), y = rnorm(100))
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(df) +
aes(x = x, y = y) +
geom_point() +
xlab(expression(hat(mu)[0])) +
ylab(expression(alpha^beta)) +
ggtitle(expression(paste("Plot of ", alpha^beta, " versus ", hat(mu)[0])))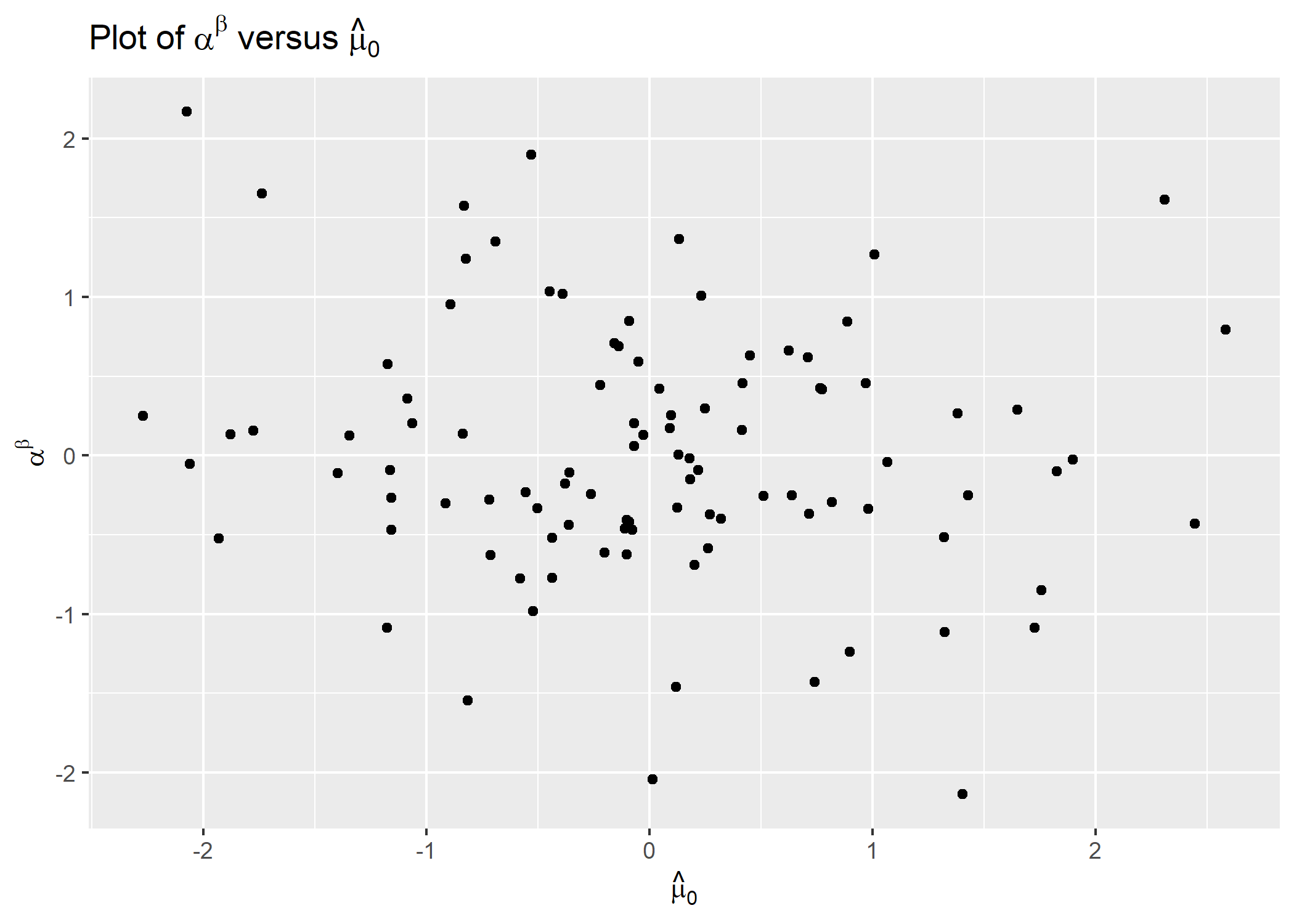
Intégrer une valeur calculée dans une expression
Pour intégrer une valeur pré-calculée, et donc stockée dans un objet R, dans une expression, on aura recours à la fonction substitute.
x_mean <- 1.5
x_sd <- 1.2
df <- data.frame(x = rnorm(100, x_mean, x_sd))
ggplot(df) +
aes(x = x) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = .25) +
ggtitle(
substitute(
paste(X[i], " ~ N(", mu, "=", m, ", ", sigma^2, "=", s2, ")"),
list(m = x_mean, s2 = x_sd^2)
)
)