chrome.permissions
| Description: |
Use the chrome.permissions API to request declared optional permissions at run time rather than install time, so users understand why the permissions are needed and grant only those that are necessary.
|
| Availability: |
Stable since Chrome 16.
|
| Learn More: |
Declaring permissions
|
Implementing optional permissions
Step 1: Decide which permissions are required and which are optional
An extension can declare both required and optional permissions. In general, you should:
- Use required permissions when they are needed for your extension’s basic functionality.
- Use optional permissions when they are needed for optional features in your extension.
Advantages of required permissions:
- Fewer prompts: An extension can prompt the user once to accept all permissions.
- Simpler development: Required permissions are guaranteed to be present.
Advantages of optional permissions:
- Better security: Extensions run with fewer permissions since users only enable permissions that are needed.
- Better information for users: An extension can explain why it needs a particular permission when the user enables the relevant feature.
- Easier upgrades: When you upgrade your extension, Chrome will not disable it for your users if the upgrade adds optional rather than required permissions.
Step 2: Declare optional permissions in the manifest
Declare optional permissions in your extension
manifest with the optional_permissions key, using the
same format as the permissions
field:
{
"name": "My extension",
...
"optional_permissions": [ "tabs", "http://www.google.com/" ],
...
}
You can specify any of the following as optional permissions:
- host permissions
- background
- bookmarks
- clipboardRead
- clipboardWrite
- contentSettings
- contextMenus
- cookies
- debugger
- history
- idle
- management
- notifications
- pageCapture
- tabs
- topSites
- webNavigation
- webRequest
- webRequestBlocking
If you want to request hosts that you only discover at runtime, include
"http://*/" and/or "https://*/" as an
optional_permission. This lets you specify any origin in
Permissions.origins as long as it has a matching scheme.
Step 3: Request optional permissions
Request the permissions from within a user gesture using
permissions.request():
document.querySelector('#my-button').addEventListener('click', function(event) {
// Permissions must be requested from inside a user gesture, like a button's
// click handler.
chrome.permissions.request({
permissions: ['tabs'],
origins: ['http://www.google.com/']
}, function(granted) {
// The callback argument will be true if the user granted the permissions.
if (granted) {
doSomething();
} else {
doSomethingElse();
}
});
});
Chrome prompts the user if adding the permissions results in different warning messages than the user has already seen and accepted. For example, the previous code might result in a prompt like this:
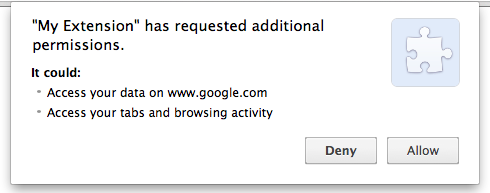
Step 4: Check the extension's current permissions
To check whether your extension has a specific permission or set of
permissions, use permission.contains():
chrome.permissions.contains({
permissions: ['tabs'],
origins: ['http://www.google.com/']
}, function(result) {
if (result) {
// The extension has the permissions.
} else {
// The extension doesn't have the permissions.
}
});
Step 5: Remove the permissions
You should remove permissions when you no longer need them.
After a permission has been removed, calling
permissions.request() usually adds the permission back without
prompting the user.
chrome.permissions.remove({
permissions: ['tabs'],
origins: ['http://www.google.com/']
}, function(removed) {
if (removed) {
// The permissions have been removed.
} else {
// The permissions have not been removed (e.g., you tried to remove
// required permissions).
}
});
Summary
| Types | |
|---|---|
| Permissions | |
| Methods | |
getAll −
chrome.permissions.getAll(function callback)
| |
contains −
chrome.permissions.contains( Permissions permissions, function callback)
| |
request −
chrome.permissions.request( Permissions permissions, function callback)
| |
remove −
chrome.permissions.remove( Permissions permissions, function callback)
| |
| Events | |
| onAdded | |
| onRemoved | |
Types
Permissions
| properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| array of string | (optional) permissions |
List of named permissions (does not include hosts or origins). Anything listed here must appear in the optional_permissions list in the manifest.
|
| array of string | (optional) origins |
List of origin permissions. Anything listed here must be a subset of a host that appears in the optional_permissions list in the manifest. For example, if http://*.example.com/ or http://*/ appears in optional_permissions, you can request an origin of http://help.example.com/. Any path is ignored.
|
Methods
getAll
chrome.permissions.getAll(function callback)
Gets the extension's current set of permissions.
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function( Permissions permissions) {...};
|
|||
contains
chrome.permissions.contains( Permissions permissions, function callback)
Checks if the extension has the specified permissions.
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permissions | permissions | ||||
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(boolean result) {...};
|
|||
request
chrome.permissions.request( Permissions permissions, function callback)
Requests access to the specified permissions. These permissions must be defined in the optional_permissions field of the manifest. If there are any problems requesting the permissions, runtime.lastError will be set.
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permissions | permissions | ||||
| function | (optional) callback |
If you specify the callback parameter, it should be a function that looks like this: function(boolean granted) {...};
|
|||
remove
chrome.permissions.remove( Permissions permissions, function callback)
Removes access to the specified permissions. If there are any problems removing the permissions, runtime.lastError will be set.
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permissions | permissions | ||||
| function | (optional) callback |
If you specify the callback parameter, it should be a function that looks like this: function(boolean removed) {...};
|
|||
Events
onAdded
Fired when the extension acquires new permissions.
addListener
chrome.permissions.onAdded.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function( Permissions permissions) {...};
|
|||
onRemoved
Fired when access to permissions has been removed from the extension.
addListener
chrome.permissions.onRemoved.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function( Permissions permissions) {...};
|
|||
