Magento 1.x Security Patch Notice
For Magento Open Source 1.5 to 1.9, Magento is providing software security patches through June 2020 to ensure those sites remain secure and compliant. Visit our information page for more details about our software maintenance policy and other considerations for your business.
Activating Web Services
Web Services give you the ability to grant permission to third-party applications to access your store data for the purpose of integration. Magento Open Source supports both SOAP and REST services.
| 1. | On the Admin menu, select System > Web Services > SOAP/XML-RPC Roles. |
| 2. | Click the Add New Role button. |
| 3. | In the Role Information section, enter a Role Name such as “API.” |
| 4. | In the panel on the left, select Role Resources. Then do one of the following: |
- To enable full access, set Resource Access to “All.”
- To provide limited access to data, set Resource Access to “Custom.” Then, select the checkbox of each resource that is available to this role.
- By default, when a area is selected, full access is granted. However, you can specify the actions that a person is allowed to take. Specific types of access are listed under many of the resource links, so it is easy to determine exactly what a user is allowed to do with the resource.
| 5. | When complete, click the Save Role button. |
| 1. | On the Admin menu, select System > Web Services > SOAP/XML-RPC-Users. |
| 2. | Click the Add New User button. |
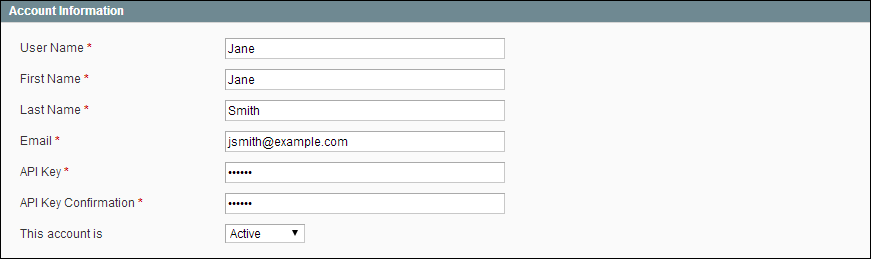
| 3. | Complete the following fields: |
- User Name
- First Name
- Last Name
| 4. | In the API Key field, type in a verification key, or password. This is the access credentials that third-party web services will use to access your Magento store. |
| 5. | To confirm, re-enter the key in the API Key Confirmation field. |
| 6. | In the panel on the left, select User Role. Then, select a role for the user. |
| 7. | When complete, click the Save User button. |
Some third-party web services rely on snippets of JavaScript code to gather data. Some web services require you to insert code in the HTML <head> section, while others require the code to be in the HTML footer, below the closing </body> tag.